The protective factors for mental health inherent to Career Technical Education (CTE) may offer opportunities to improve mental health and overall outcomes for learners, solidifying CTE’s role in not only preparing learners for the workforce but also for life. In part two of this four-part blog series, Senior Communications Associate and Mental Health Educator Jodi Langellotti shares research on the power of hope and positive childhood experiences (PCEs) to buffer the negative effects of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs).
In the first blog in this series, we discussed how 80% of our most common health, social, and behavioral challenges are a direct result of trauma experienced in childhood. This trauma, also referred to as adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), results in changes in the developing brain that can result in challenges with focus, attention, emotional regulation, executive functioning skills, and more. The original ACEs study from the mid-1990s showed that ACEs are common, they are interrelated, and that those who experience more trauma in childhood, as evidenced by a higher ACE score, are at greater risk for negative life outcomes including disease, mental health challenges, incarceration, substance use challenges, and more.
The Life Progression of Adversity
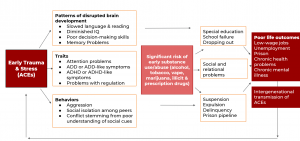
Recreated by the author based materials from the ACE Interface Master Trainer Training
When we look at the life progression of those who are affected by ACEs and the resulting disrupted brain development, traits, and behaviors, we see a significant increase in the risk of early substance use as a coping mechanism (see chart above). For example, nicotine found in cigarettes and vape products can reduce anxiety and help to increase focus and attention. For someone challenged with attention problems and/or anxiety, smoking or vaping may improve those conditions and be an attractive coping mechanism despite the known associated health risks. This increases the person’s risk for chronic smoking-related health problems later in life, like cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and emphysema.
Even if a young person does not turn to substance use as a coping mechanism, there is still a significant risk of negative outcomes as a result of the changes in brain development as depicted in the image below. When those with ACEs have children, the risk of transmitting that adversity to their children is significantly higher when they continue to suffer from the impact of the adversities they have faced.
The Role of Hope and Support
When people feel that they have hope and support, the negative effects of adversity are significantly reduced. In the chart below, you can see that the percentage of respondents who experienced poor mental health for half of the last 30 days drops drastically when they felt they had hope and were supported, regardless of how much adversity they have experienced. This important factor, the role of hope, is often left out of ACE conversations and presentations though it is the primary reason that a person’s individual ACE score is not predictive of their individual life outcomes. Both ACEs and the role of hope and support have a dose-response relationship, the greater the dose, whether it be toxic stress or hope and support, the greater the impact.
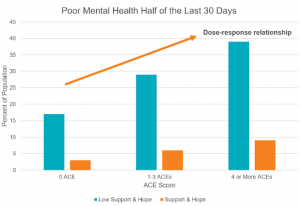
Recreated by the author based on materials from the ACE Interface Master Trainer Training
In 2019, new research on resilience and positive childhood experiences (PCEs) through Johns Hopkins University lead by principal researcher Dr. Christina Bethell provided statistical evidence that hope and support can buffer the negative effects of adverse childhood experiences.
The study, conducted with over 7,000 participants aged 18+, involved asking participants a variety of questions about childhood trauma, their mental health, and the health of their relationships. It is important to note, that the questions regarding trauma were not limited to the 10 ACE categories and therefore were more reflective of additional modern-day forms of trauma one may experience.
The findings of the PCEs study identified seven positive childhood experiences or protective factors that have a lifelong beneficial, ripple effect on mental health and overall life outcomes.
These PCEs can be categorized as taking place within the home and within the community, to include the school community:
Within the home
- Able to talk to family about feelings
- Felt family stood up for them in difficult times
- Felt safe and protected by an adult in your home
Within the community
- Had at least two non-parent adults who took genuine interest
- Felt supported by friends
- Felt a sense of belonging in school
- Enjoyed participating in community traditions
The PCEs study showed that positive experiences have a similar dose-response relationship as adverse experiences – the more positive experiences, the better the chance for positive mental and relationship health despite the level of adversity or trauma experienced. The PCEs study confirmed that positive childhood experiences can buffer adverse childhood experiences thereby reducing the neurological, emotional, and behavioral impact of ACEs.
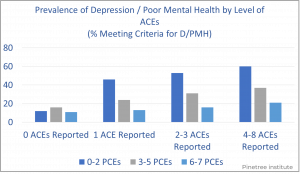
Source: Pinetree Institute
The Role of Career-connected Learning on Learner Hope and Engagement
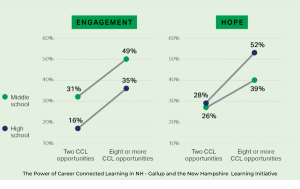
In a report released in September 2023, Gallup reported that there is a direct connection in the number of career-connected learning (CCL) opportunities experienced and a learner’s engagement and hope. This study, performed in the spring of 2023 by Gallup and New Hampshire Learning Initiative (NHLI), surveyed more than 9,600 students in fifth through 12th grades across 28 schools in 13 districts throughout New Hampshire. Significant findings include:
- Mentors matter for hope. Those who agree they have a mentor who supports their development are more likely to be hopeful about the future than their peers who do not have such a mentor (40% vs. 25%).
- Engagement matters. Even students with lower academic performance who were more engaged through CCL reported having a higher sense of hope that they will graduate high school.
- There is a dose-response relationship between the number of CCL opportunities and the rate of engagement and hope. The more CCL opportunities, the higher the student’s engagement and sense of hope.
Looking Ahead
In the next blog in this series, we will discuss the importance of relationships in buffering the effects and intergenerational transmission of adversity and the inherent aspects of CTE that serve as protective factors for mental health.
Future blogs in this series will discuss:
- Communicating CTE as a protective factor and continuing the conversation
Resources
- Adverse Childhood Experiences: Prevention for Action, Centers for Disease Control https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/pdf/ACEs-Prevention-Resource_508.pdf
- Healthy Outcomes from Positive Experiences: Positive Childhood Experiences and Adult Mental Health: https://positiveexperience.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/BRFShandout2-18.pdf
- Positive Childhood Experiences and Adult Mental and Relational Health in a Statewide Sample Associations Across Adverse Childhood Experiences Levels: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2749336
- Research Round-up: Impact of Career-Connected Learning on Learner Engagement and Hope https://blog.careertech.org/research-round-up-impact-of-career-connected-learning-on-learner-engagement-and-hope/
- The Power of Career Connected Learning in NH: https://nhlearninginitiative.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Gallup-New-Hampshire-Learning-Initiative_-Report_2023.pdf
Much of the information in this blog is from the author’s training as an Adverse Childhood Experiences Master Trainer through ACE Interface with Dr. Robert Anda and Laura Porter and through her volunteer work within the community mental health space.
